The use of malicious software to encrypt files on victims’ computers and demand payment in exchange for the decryption key is a common form of cybercrime known as ransomware attacks. These assaults can cause huge harm to the two people and organizations, with potential outcomes going from information misfortune to monetary ruin.
In this article, we’ll have a careful dive into the particulars of how ransomware assaults work and investigate the prescribed procedures for forestalling them.
How does Ransomware work?
Ransomware attacks are a common type of cybercrime in which the attackers encrypt files on the computers of their victims with malicious software and demand payment in return for the decryption key. These attacks have the potential to severely harm individuals as well as businesses, resulting in data loss and financial ruin.
We’ll take a thorough look at the ins and outs of ransomware attacks and the best ways to avoid them in this article.
Most of the time, this kind of attack starts with an innocent user clicking on a link or downloading an attachment that has malware in it. The delivery methods of ransomware attacks can use a variety of ways and take many different forms.
- Email phishing tricks to fool clients into clicking on links or downloading connections that contain the malware.
- Spreading through malicious websites and social media channels.
- Spreading through public Wi-Fi access.
- Spread through portable drives.
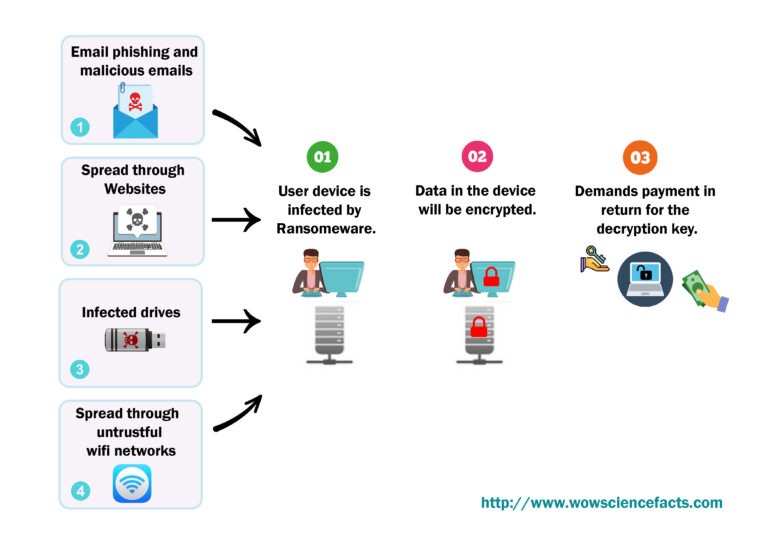
Once the malware is installed, it starts encoding documents on the client’s PC. The attacker then, at that point, requests something in his need in return for the decryption key that will decode the encrypted documents. Thant is how it works as in Figure 01. Let’s now see how to stop these kind of ransomware attacks!
How to Avoid Ransomware Attacks!
Forestalling ransomware assaults is a fundamental way of shielding your PC and your valuable file and information from cybercriminals. Fortunately, you can reduce the likelihood of an attack by following a number of best practices. The most efficient strategies for avoiding ransomware attacks are listed below:
Another effective strategy for avoiding ransomware attacks is to make use of anti-virus and anti-malware software. Before ransomware can infect your system, these programs can identify and remove malicious software. Run regular system scans and make sure your antivirus and anti-malware software are up to date to find any potential threats.
Antivirus and anti-malware software is available in a wide variety of flavors, from free alternatives to expensive software bundles. Norton, McAfee, and Avast are a few well-known choices. Regardless of the software you choose, ensure its effectiveness and dependability.


An attacker’s ability to guess weak passwords makes it easier for them to access your system and install ransomware. Use strong passwords with a mix of letters, numbers, and symbols that are at least 12 characters long to prevent this. Also, think about turning on two-factor authentication, which requires a second type of authentication, like a fingerprint or a code sent to your phone, to increase security.
To create a more complex password, avoid using common words or phrases and try to mix up the character types. For instance, rather than utilizing “password123,” think about utilizing a blend of capitalized and lowercase letters, numbers, and images to make a safer secret phrase like “P@ssw0rd!23
Another effective strategy for avoiding ransomware attacks is to regularly back up your data. Having a recent backup of your files can help you recover your data without paying a ransom in the event that your computer is infected with ransomware. Backup your data to a safe location, such as an external hard drive or a cloud storage service, to ensure its safety.
While supporting your information, ensure you follow best practices to guarantee that your reinforcement is secure. If an attacker gains access to your backup location, for instance, encrypting your backup can assist in preventing them from accessing your data.

Numerous ransomware assaults are conveyed through email phishing tricks. When opening emails and attachments, especially if they come from unknown senders, be cautious to avoid these kinds of attacks. Never respond to an email request for personal information, and never click on links or download attachments from suspicious emails.
Be aware of the warning signs of a phishing email to avoid falling for phishing scams. Check the sender’s email address for legitimacy, look for typos or grammatical errors, and be wary of urgent requests or offers that seem too good to be true.
A firewall is a security system for the network that controls and monitors both incoming and outgoing traffic. By restricting access to your system and preventing suspicious network activity, a firewall can help prevent ransomware attacks. There are a lot of operating systems that come pre-installed with firewalls; however, there are also a lot of third-party firewall applications out there that provide additional security features.
To ensure that a firewall is effectively protecting your system, make sure its configuration is correct. If you want to make sure that your firewall is properly set up and protects your data to the fullest extent possible, you might want to consult an expert in cybersecurity.


At long last, schooling is critical to forestalling ransomware assaults. Make sure you and your team are well-versed in the most effective methods for avoiding ransomware attacks, such as those described in this article. Moreover, consider giving network safety preparation to your group to guarantee that they know about the dangers and ability to forestall assaults.
You can significantly lower the likelihood of a ransomware attack on your computer or network by following these best practices. In any case, it’s memorable critical that no framework is totally idiot proof, and assailants are continually advancing their strategies to remain in front of online protection measures. As a result, it is necessary to maintain vigilance and keep up with the most recent cybersecurity threats and best practices.
Attackers can use vulnerabilities in out-of-date software and operating systems to deliver ransomware and gain access to your system. Installing patches and updates as they become available is essential to keeping your software and operating system up to date and preventing this.
Automatic updates are available in a lot of software and operating systems, which can make this process easier. In any case, it’s yet critical to routinely check for refreshments and introduce them quickly to guarantee that your framework is shielded from the most recent dangers.

Last but not least, carrying out a security strategy can help forestall ransomware assaults by laying out clear rules and methods for safeguarding your framework and information. Guidelines for managing passwords, controlling access, and protecting a network’s security are all possible components of a security policy.
Make sure that all employees and stakeholders are aware of and adhere to the guidelines in your security policy, which should be comprehensive and up to date. Your security policy’s effectiveness in protecting against the most recent threats can also be maintained by reviewing and updating it on a regular basis.
Conclusion
Some quick notes:
Cybercriminals use ransomware, a type of malicious software, to prevent you from accessing your own data. The digital extortionists encrypt and add extensions to the attacked data on your system before holding it “hostage” until the demanded ransom is paid.
Ransomware is malware that encodes a casualty’s significant records popular of an installment (deliver) to reestablish access. A decryption key is given to victims of ransomware if they pay the ransom.
A type of malicious software known as ransomware infects a computer and prevents users from accessing it until they pay a ransom to unlock it. Variants of ransomware have been around for a while, and they frequently use an on-screen alert to try to get money from victims.
Ransomware infections are typically brought on by phishing, exploiting remote desk protocol (RDP), and software flaws.
Ransomware can encode significant documents and render them futile. Businesses may experience serious issues as a result, including the loss of customer data or private company information. Last but not least, ransomware attacks can also harm a company’s reputation.
