Why do some websites not have www?
Short answer: Actually “www.” is the subdomain. For an example “www.example.com” is a subdomain of “example.com” main domain. What actually does usually is either of the domains are selected as main domain (canonical form) and make others to redirect to the main domain for convenience of the user. Conventionally, the “www” subdomain, contains the main website. This has a historical background which we will be discussing in the first part of the article.
In this article we discuss:
Why WWW?
The World Wide Web (www) was invented after the internet. By then, the internet used to be mainly used for emails, file transfers between universities, and remote-terminals. When the “web” came along, people bolted a webserver to their domain and made it accessible at the www subdomain, as a convention to signify a publicly accessible web portal.
Subdomain “www”, we can say it is kind of a department. For example, “blog.example.com” and “maps.example.com” are both subdomains of the “example.com” root domain. Subdomains are free to create under any root domain. Ok now the question is that “What is root domain?”. There is confusion what actually is root domain. First lets checkout the sections of a domain. Having said that, first let’s take a look at the key sections of a domain name,
Components of an URL:
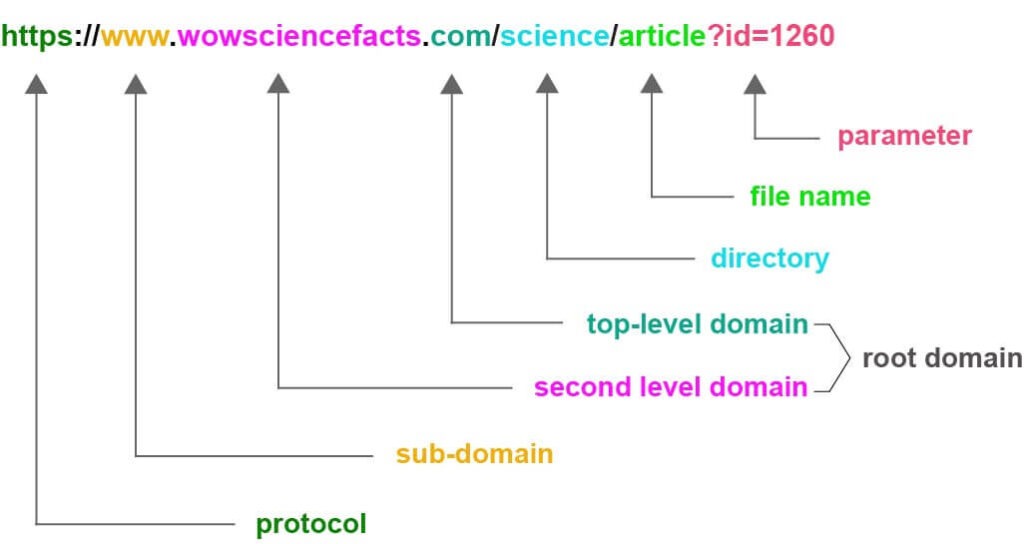
◉ Top-level domain (TLD): examples are ‘.com’, ‘.org’, ‘.net’, etc. From them, ‘.com’ is being most famous 48% of domain names use it as their TLD.
● Country or region specific TLDs such as .au, .uk, .nz .eu are called Country-code top-level domain (ccTLD)
For more info, the list of all TLDs is in this link:
◉ Second-level domain (SLD): After the TLD this is where one can get their domain name customization. If you’re a business, company or organization, it’s best to place your brand name within your SLD. Since it is unique with given TLD, your desired SLD may be already being registered. This is also known as Domain name.
Root Domain: Term “root domain” is often interchangeably use to identify two scenarios technically depending on the context whether domain name or hierarchy. In domain name, “root domain” refers to the main domain name of the site, in alternative expression more technically the combination of SLD + TLD. This combination is considered as an asset in virtual world. Buying, holding and reselling of root domains are commonly done by the most of the cyber asset holders. Another such popular e-asset those type of e-asset holding people hold is NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens).
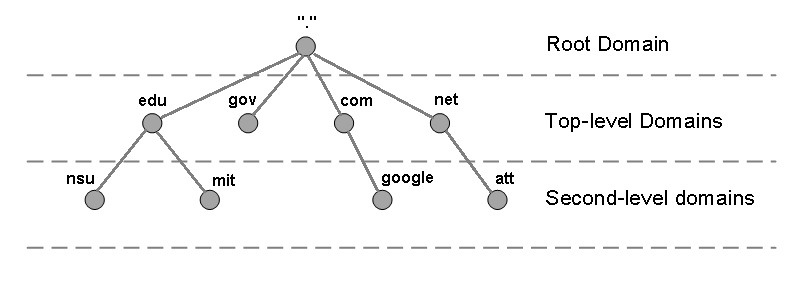
Domain name hierarchy
In domain name hierarchy root domain (sometimes called the zero-level domain) refers to empty character and denoted by a dot (.). That means that the root domain is an empty name. Thus it is the highest hierarchical level of the internet.
Additionally, if this dot is present in a domain (for example “www.example.com.”), then the domain name is considered complete (absolute). If there is no dot at the end of the name (“www.example” or “www.example.com”), the name is considered relative.
Subdomain: These are the third level of a domain level hierarchy point of view (Figure 2). Those are added in front of the root domain and separated by a dot (period) from the root domain.
As mentioned earlier at the beginning of the article, these subdomains are free to create using the DNS provider web portal. For example, if a domain offered a blog/app as part of the website example.com, it might use the subdomain blog.example.com/ app.example.com for blog and app respectively.
The answer for topic “why do some websites not have www” exactly lies here. ‘WWW’ is also a subdomain of the domain name. Thus, for any root domain (SLD + TLD : link to root domain paragraph) subdomain www can be added. Now it should be clear that what is the function of www where is comes from and “why do some websites not have www”.
Bonus Topic
To give complete understanding of the URL as a side note let’s find out what are query parameters n URL. (see: Figure 1) The query parameters lies after the domain path to the page and those are starting with “?”(? is refered to as start string). Thus, it marks the start of query field-parameters (key) and value pairs separated by ampersand “&” if there are multiple key value pairs. Now, when you see a URL it should be clear now what this address contains of.